Algebra (ring theory)
In mathematics, specifically in ring theory, an algebra over a commutative ring is a generalization of the concept of an algebra over a field, where the base field K is replaced by a commutative ring R.
In this article, all rings are assumed to be unital.
Contents |
Formal Definition
Let R be a commutative ring. An algebra is an R-module A together with a binary operation [·, ·]
called A-multiplication, which satisfies the following axiom:
- for all scalars a, b in R and all elements x, y, z in A.
Associative Algebras
If A is a monoid under A-multiplication (it satisfies associativity and it has an identity), then the R-algebra is called an associative algebra. An associative algebra forms a ring over R and provides a generalization of a ring. An equivalent definition of an associative R-algebra is a ring homomorphism 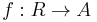 such that the image of f is contained in the center of A.
such that the image of f is contained in the center of A.
See also
- associative algebra
- commutative algebra
- Lie algebra
- semiring
- split-biquaternion (example)
- Example of a non-associative algebra (example)
References
- Lang, Serge (2002), Algebra, Graduate Texts in Mathematics, 211 (Revised third ed.), New York: Springer-Verlag, ISBN 978-0-387-95385-4, MR1878556
![[\cdot,\cdot]: A\times A\to A](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/25a2f67f696b93bccc8b87c21f26491c.png)
![[a x %2B b y, z] = a [x, z] %2B b [y, z], \quad [z, a x %2B b y] = a[z, x] %2B b [z, y]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/50d637f47c6fa9abec81c24abb5b7872.png)